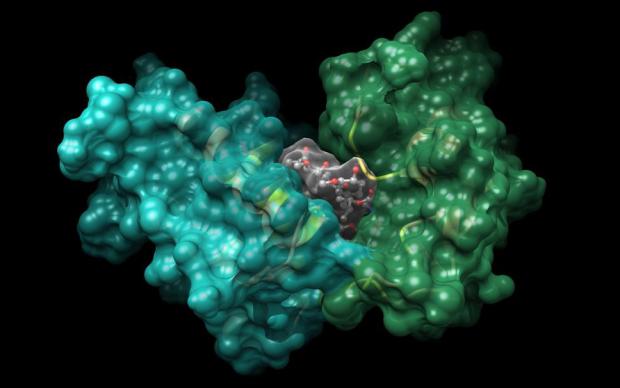
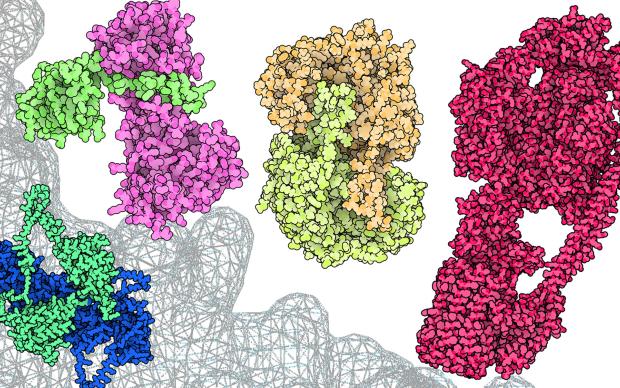
Bioinformatics resources, such as those developed at SIB, enable scientists worldwide to study life and foster discoveries. Discover the stringent selection process guiding their inclusion in the institute’s portfolio of leading open biodata resources, and the professional support they benefit from throughout their life cycle. Our unique model helps these essential databases and software tools to reach and maintain the highest level of usefulness, accuracy and reliability for their over 10 million yearly users. Most of SIB Resources have received international recognition.
A portfolio of essential bioinformatics resources
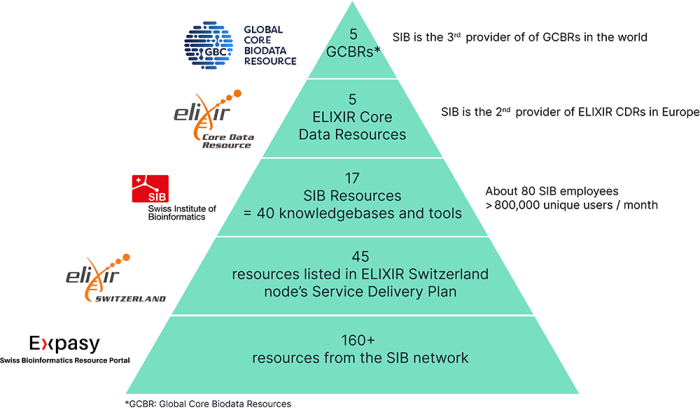
Over 160 tools and databases are developed by the SIB community and openly available on Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal. Among them, 17 are designated as SIB Resources. They are made up of 40 software tools and databases. These leading open biodata resources are >selected to ensure the highest quality is delivered to the global life sciences community.
More about SIB’s support throughout the resources’ life cycle
The need to foster high-quality open resources
Research and activities in the life sciences produce massive volumes of fundamental data which are difficult to reproduce. Open biodata resources in the form of software tools and databases play a crucial role in enriching these fundamental data with curation and analyses, but also in facilitating their analysis and visualization in various contexts. By enabling the preservation of knowledge, ensuring reproducibility, and driving impactful research, bioinformatics resources significantly enhance the quality of science.
Recognizing this, since 2000 the State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI) has provided SIB with the mandate and the funding to identify, support and develop essential open bioinformatics resources.
Discover the impact of SIB Resources in tackling global challenges
Browse our portfolio
Browse the SIB portfolio below, and visit Expasy, the Swiss bioinformatics resource portal, for the complete set of resources developed by our community.

- A software tool for automated single-cell data analysis
- Bart Deplancke group

- A cross-platform program for Bayesian phylogenetic analysis of molecular sequences
- Tanja Stadler group
- Watch the in silico talk
- Discover the newest SIB Resources in 2025

- An expertly-curated gene expression database
- Marc Robinson-Rechavi and Frédéric Bastian group
- Read about venom factories: a surprising molecular convergence, from wasps to snakes
- Bgee is a Global Core Biodata Resource

- An expertly curated database on cell lines
- Amos Bairoch and Lydie Lane group
- Read the article in Le Temps
- Cellosaurus is an ELIXIR Core Data Resource and a Global Core Biodata Resource

- Portal of expertly curated databases and software tools for glycoinformatics
- Includes GlyConnect and UniLectin
- Frédérique Lisacek group

- A microbial taxonomic profiler and genome database
- Shinichi Sunagawa group
- Discover the newest SIB Resources in 2025

- A software tool to track pathogen evolution in real-time
- Includes Nextclade
- Richard Neher group

- An expertly curated database of biochemical reactions
- Alan Bridge group
- Rhea is an ELIXIR Core Data Resource and a Global Core Biodata Resource

- A database of known and predicted protein-protein interactions
- Christian von Mering group
- STRING is an ELIXIR Core Data Resource and a Global Core Biodata Resource

- A suite of web-based computer-aided drug design software tools
- Includes SwissDock, SwissParam, SwissSidechain, SwissBioisostere, SwissTargetPrediction, SwissSimilarity, SwissADME
- Olivier Michielin & Vincent Zoete group
- Watch the course

- An expertly curated database of lipids
- Alan Bridge group
- Watch the tutorial
- A protein structure homology-modelling suite of software tools and databases
- Includes Continuous Automated Model EvaluatiOn (CAMEO), ModelArchive, SWISS-MODEL Server, SWISS-MODEL Repository
- Torsten Schwede group
- Read about facilitating access and reuse of computer-predicted protein structures with ModelArchive
- ModelArchive is an ELIXIR Deposition Database
- SWISS-MODEL is an ELIXIR Core Data Resource

- A one-stop shop for orthologs
- Includes Orthologous Matrix (OMA), OrthoDB, BUSCO (Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs), Orthology Benchmarking
- Christophe Dessimoz & Natasha Glover and Evgeny Zdobnov & Evgenia Kriventseva
- Watch the in silico talk
- Read about how asexual reproduction affects the evolution of genomes

- A One-Health online platform for real-time sharing of pathogen sequencing data
- Valérie Barbié and Aitana Neves group
- Read how SPSP is at the heart of Swiss disease control strategy
- Discover the newest SIB Resources in 2025
- A regulatory genomics portal
- Includes Integrated System for Motif Activity Response Analysis (ISMARA), Cis-Regulatory Element Motif Activities (CREMA), Reference sequence Alignment based Phylogeny (REALPHY), Phylogibbs, CRUNCH, Dinucleotide Weight Tensors (DWT) Online, Two-component Systems (TCS), Bonsai
- Erik van Nimwegen group
- Watch the tutorial

- An expertly curated database of proteins
- Alan Bridge group
- UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot is an ELIXIR Core Data Resource and a Global Core Biodata Resource
- A software tool for the analysis of viral high-throughput sequencing data
- Niko Beerenwinkel group
- Watch the in silico talk
A robust selection process involving international experts
SIB has developed a robust selection model allowing the best databases and software tools in the Swiss life science landscape to be recognized and supported by the institute. Every four years, our independent Scientific Advisory Board (SAB) recommends which resources from the SIB community should be included in the institute's portfolio. Its recommendations are based on their scientific impact as well as the scientific return on investment and consistency with the institute’s strategy. The SAB also provides guidelines for their continuous development that are monitored every two years. The level of support in terms of allocation of funding and employees to implement the action plan is then decided by SIB’s Board of Directors.
The assessment and monitoring of the SIB Resources is done across a set of around 30 indicators every four years

The SIB Scientific Advisory Board
As a leader in bioinformatics and a provider of world-class biodata resources, SIB has established a Scientific Advisory Board to select and guide the development of its portfolio’s tools and databases in line with the Institute's strategy. This board brings together internationally renowned scientists from a wide variety of life science domains.
Customizable to industry needs
All SIB Resources can be tailored to specific needs or proprietary data. For instance, the orthology database OMA, part of SwissOrthology, was customized to the needs of the chemical company BASF. This enables them to develop various traits in crops such as soybean and wheat, by inferring homologous relationships between genes using both public and proprietary genome sequences.
Professional support for long-term sustainability
SIB Resources are continually supported through their life cycle to reinforce their impact and quality. A virtuous circle is thus created where it is more likely that they will receive additional funding from other sources in future, thus ensuring their sustainability. This is coordinated by the Biodata Resources team and involves other teams in SIB's support functions. Unique in academia, this dedicated service offering includes technical support, best practices and knowledge sharing, infrastructure hosting, user experience, legal and data protection human resources and grant management.
Managing the life cycle of SIB’s portfolio of open data resources
SIB’s selection process focuses on resources that have passed the proof-of-concept stage, and which are often funded as part of research projects. The institute supports the growth of resources that are thus defined as emerging or mature. It also helps them to gain recognition at the international level.
Read the complete article describing this process
When a SIB Resource ceases its activity – for lack of sufficient funding, retirement or move of the Principal Investigator outside of Switzerland - the institute also ensures that the most important resource assets remain available to the life sciences community.
Resources currently recognized at the European and worldwide levels
5 SIB Resources are recognized at the European level as ELIXIR Core Data Resources (Cellosaurus, Rhea, STRING, SWISS-MODEL and UniProt) and 5 are designated as Global Core Biodata Resources (Bgee, Cellosaurus, Rhea, STRING and UniProt) thus being recognized worldwide. This positions Switzerland as the 2nd leading provider of ELIXIR CDRs in Europe as well as the 3rd provider of GBCRs worldwide.
Aiming for international recognition as biodata infrastructure
Being hosted on Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal represents the primary support offered by SIB to nurture the tools and databases developed by its members. As they mature, they can be included in ELIXIR Switzerland’s Service Delivery Plan, a selection of long-term, sustainable, and high-quality services produced by the Swiss bioinformatics community. They then have the potential to become SIB Resources, benefitting from long-term dedicated professional support and funding. Resources that demonstrate their value to the international community can be further recognized on a European level through inclusion in ELIXIR Core Data Resources, and even worldwide, as Global Core Biodata Resources.
Such recognitions are a great tribute to the SIB Groups developing them, demonstrating their continued fundamental importance to the worldwide life sciences community as well as SIB’s commitment to life science infrastructure and to Switzerland’s leading expertise in biological data.
Ensuring SIB Resources remain at the cutting-edge
To ensure that resources remain at the cutting edge of research, whether on the user experience, scientific content or interoperability fronts, the Biodata Resource team ensures the follow-up and supports the implementation of the recommendations delivered by the Scientific Advisory Board. This includes helping to set up user surveys, advising on improving the FAIRness of resources as well as the monitoring of KPIs and analytics, UX design improvement, initiating funding projects to develop new scientific ideas and fostering collaborations within the portfolio and with the SIB network:
- Read how, on a recommendation of the SAB, a STRING user survey was crafted, and new features developed as a result – making STRING the only resource offering such complete service;
- Five projects were selected after a call to use artificial intelligence to increase the impact of the SIB Resources. These projects bring together SIB groups specialised in AI/ML with SIB Resources;
- Interoperability among SIB Resources is key to lead to new discoveries, by linking different types of high-value datasets (e.g. SPARQL endpoints in Expasy).
- To foster the adoption of best practices in term of open licencing, our Legal and Technology Transfer Office works closely with SIB Resources and issues guidelines for the community. If you are from the industry and looking to collaborate or tailor a resource to your need, contact us.